Scientific report
Activity Report 2018
A1.1. Modelling the TiO2-rGO, WO3-rGO oxide nanostructures and their combinations
By associating metallic oxide semiconductors with rGO, e.g. TiO2-rGO and WO3-rGO composite structures, respectively, a shift from UV to VIS-activation of the semiconductor is possible with optimal loading of the metal oxide on the reduced graphene oxide. A comprehensive study of the scientific literature on the opto-electrical and morphological properties of the composite systems based on TiO2-rGO and WO3-rGO was done. As a result of this study, the following recommendations were made:
- the WO3:rGO ratio should be 100:x where x=0.1..3% (mass) rGO;
- the TiO2 : rGO ratio should be 100 : x, where x = 0.1-1% (mass) rGO;
- the annealing temperature should be in the 70-500oC according to the method used to obtain the thin film; the temperature should not suprass 100oC if the thin films are obtained from sol-gel powders in which rGO was added to the precursor system of the metallic oxide;
- along X ray diffraction, FTIR analysis should be employed to test the presence of rGO in the obtained powders or thin films, as the quantity is rather small.
A1.2. Synthesis and characterization of the nanostructured TiO2-rGO powders
Sol-gel TiO2 and TiO2-rGO powders were obtained starting from titanium tetraisopropoxide in water-ethanol solvent through two routes (by adding rGO in the precursor solution or by milling it with the pristine TiO2 powder before dispersing it in water-ethanol, during A1.4) with the purpose of controlling their structural and morphological properties. Sodium dodecylsulfate was used as additive at concentrations below and above its critical micelle concentration. Correlations between the annealing temperature (100oC, 200oC, 300oC and 550oC) and the powder structure were established.
After annealing at 550oC, the crystallinity of the samples was good and anatase phase was evidenced by XRD. FTIR analysis also evidenced the presence of bonds specific to rGO. By adding rGO to the optimized TiO2 powders, the annealing treatment was lowered to 100oC to maintain the rGO structure (as verified by FTIR measurements).
Three powders were selected to be used further to obtain stable dispersions, namely TiO2 annealed at 550oC, TiO2+rGO annealed at 100oC with 0.1% rGO and 0.2% rGO;
A1.3. Synthesis and characterization of the oxide powders based on WO3-rGO
Sol-gel tungsten oxide powders were obtained from tungsten chloride in water-ethanol mixture, using acetyl acetone or polyethyleneglycol 400 as additives. Similar to the case of TiO2, two routes were used to obtain the powders. Fine, crystalline WO3 powders were obtained as confirmed by XRD, EDX and SEM analyses. Similar to TiO2, the addition of rGO to the sol requires a decrease in the thermal treatment temperature of the powders from 550 to 100oC with a decrease in crystallinity from ~ 66% to ~10%, when the acetylacetone additive was used.
Two powders were selected to be used in the dispersion formulation, namely WO3 annealed at 550oC and WO3+rGO with the ratio 100:1 annealed at 100oC.
A1.4. Synthesis, characterization, optimization of the dispersions from TiO2-rGO and WO3-rGO powders and stability correlations
Dispersions were obtained from the previously optimized powders, but also from mixing pure and highly crystalline metal oxide powders with solid rGO. The influence of the following parameters on the dispersions’ stability was investigated: the chemical composition of the continuous medium (water-ethanol ratio), the dispersed phase concentration (0.1-0.5%) and the stabilizator type (anionic, cationinc surfactant, polymer).
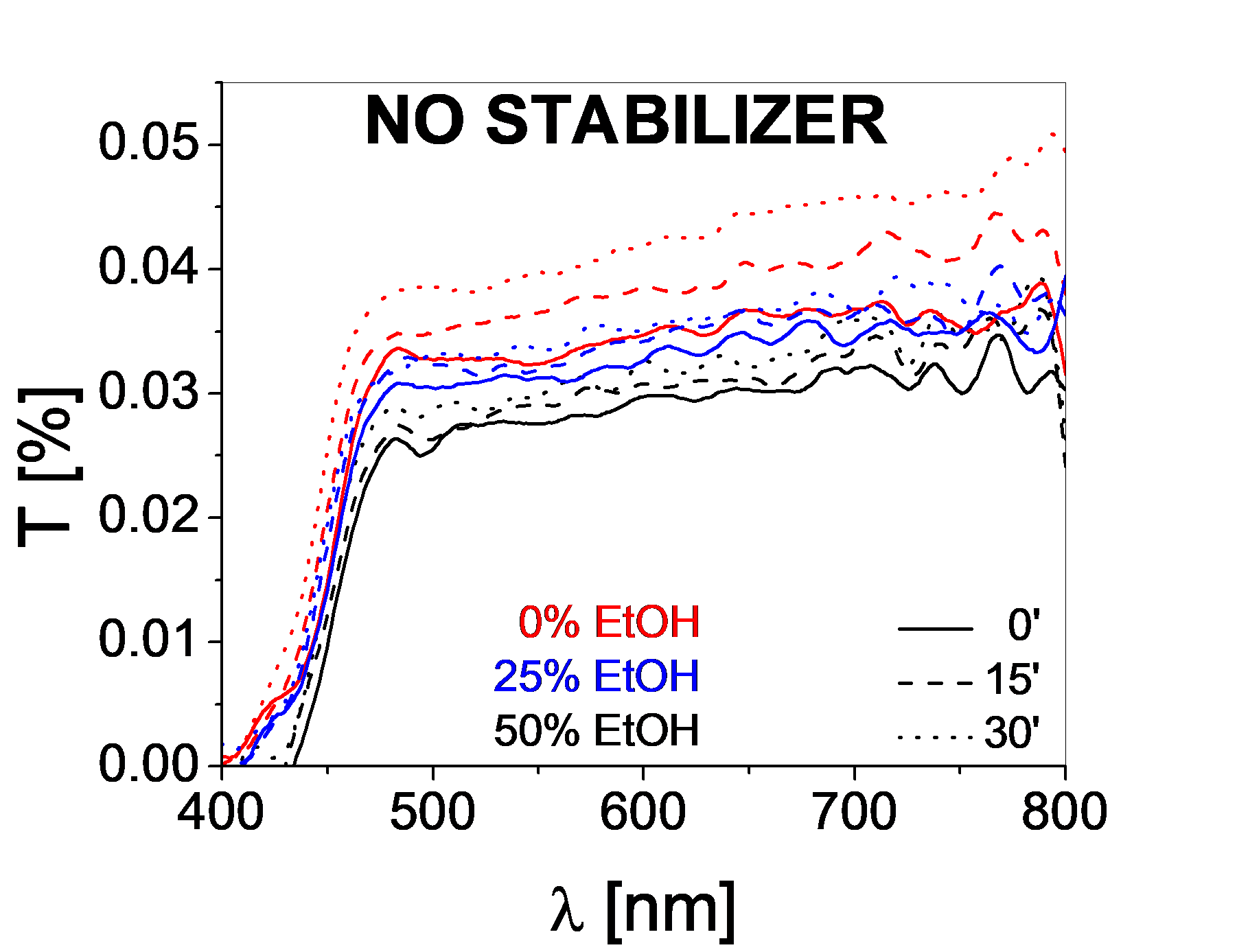
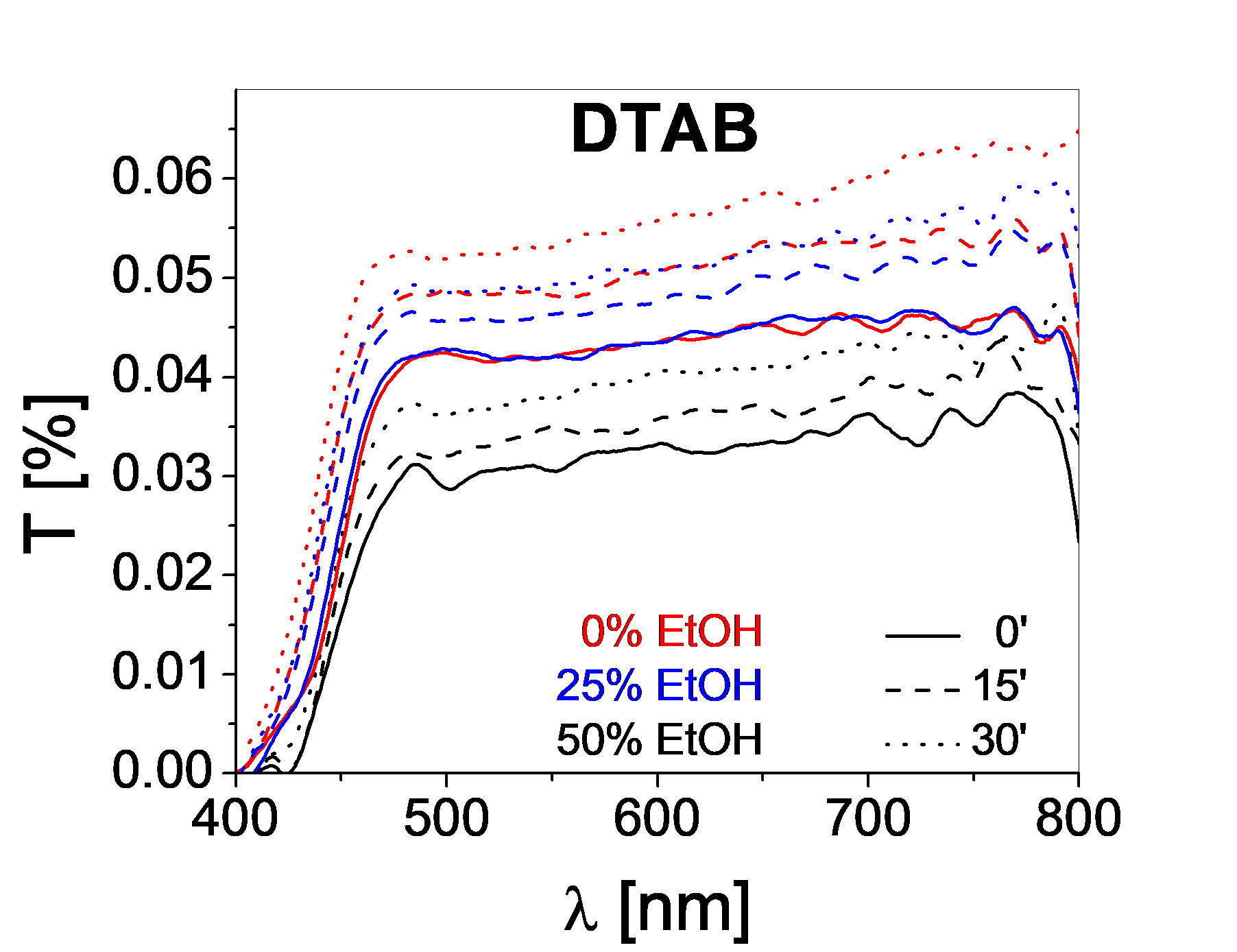
The stability of the dispersions in water-ethanol (variable mixtures: 0, 25, 75% EtOH), using different stabilizers (dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide - DTAB, sodium dodecylsulfate - SDS, polyethylene glycol - PEG) was evaluated through transmittance measurements.
Both in the case of TiO2+rGO as well as in the case of WO3+rGO, the optimum concentration of ethanol in the continuous medium is 25%. The best stability (lowest ΔT) for the WO3-rGO, after 30 minutes, was obtained when using SDS.
 |
 |
|
 |
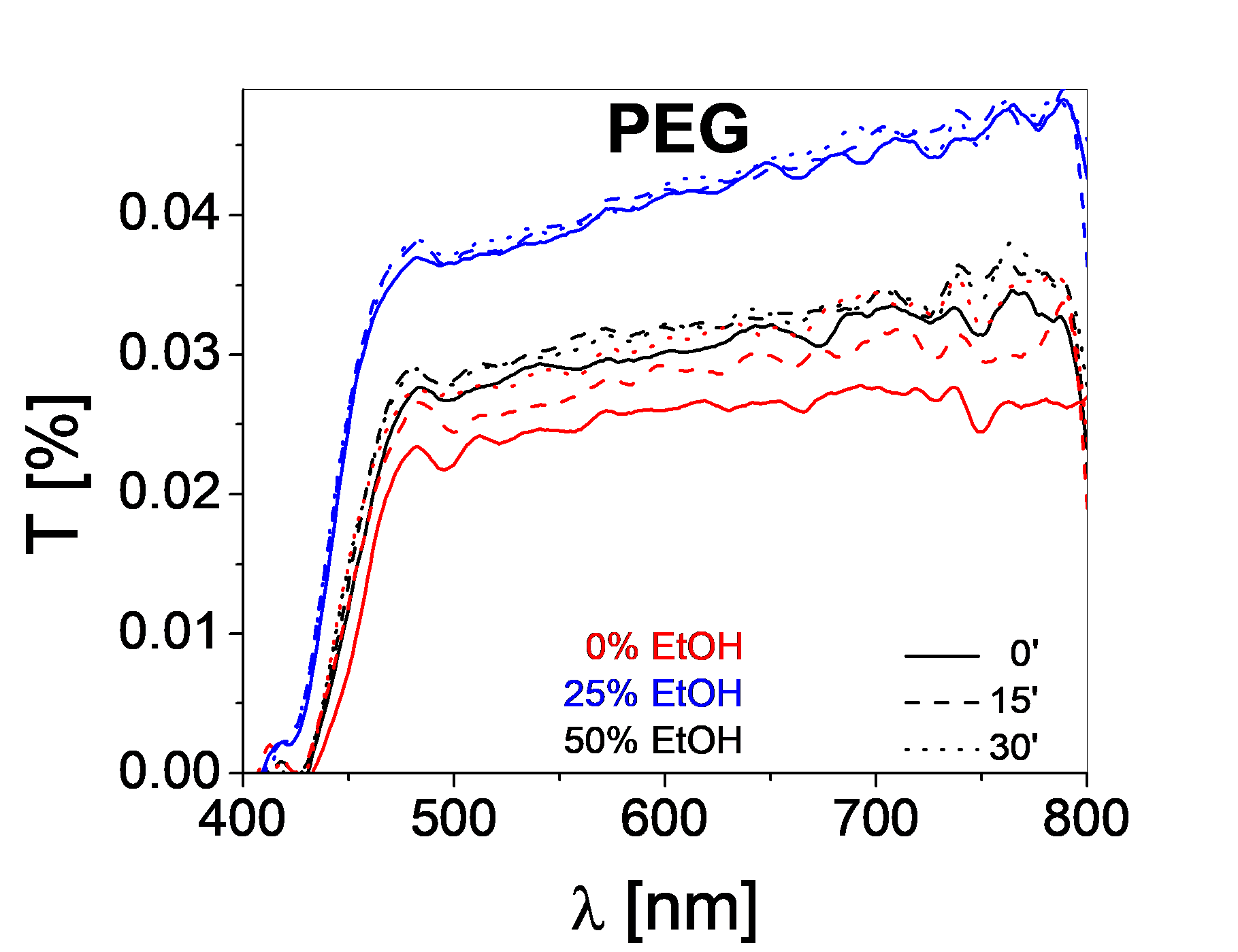 |
The best stability for the TiO2-rGO powders was obtained when using DTAB due to surfactant-TiO2 electrostatic interactions (attraction), as well as surfactant hydrophobic tail-rGO bonding.
These results correspond to a dispersed phase concentration of 0.5% for both the TiO2+rGO and the WO3+rGO based dispersions.
A1.5. Deposition, characterization and optimization of the thin films deposited on small-sized substrates
Thin films were deposited on small scale glass substrates from the previously optimized dispersions, through spray deposition, by varying the spraying sequence (layer) number (8-10 layers for TiO2+rGO films and 5-8 layers for WO3+rGO). Correlations between the dispersion stability and the structural, morphological, optical, wetting and photocatalytic properties of the thin films were done, keeping in mind the key performance indicators set for the multifunctional thin films with IR-S, AR and SC properties.
Good self-cleaning properties were obtained for the WO3+rGO thin films using dispersed powders annealed at 550oC. Superhydrophilic (θ=2..6o) WO3-rGO thin films were obtained through spray deposition of high-transmittance glass. Photocatalytic degradation efficiency of methylene blue reached ~30% after 8 hours, under solar simulated radiation. Slightly lower values for phenol can be due to the formation of polyphenols as photocatalysis by-products.
Thin films, especially the TiO2-rGO, showed good anti-reflectance properties (TUV-VIS>80%, RUV-VIS=15..20%). Anti-reflective properties need to be improved through thin film morphology tailoring.
In 2019, the IR-S properties of the individual films will be optimized, as well as obtaining mixed WO3-TiO2-rGO thin films with improved, synergistic properties. Alternative film deposition through sol pulverization directly on the solar glass, followed by thermal treatment is under work.
A1.6. Dissemination in 2018
The project results were disseminated in:
- Two presentations at an international conferences (Catalysis Conference CAT-2018, 20th Workshop on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, NANO 2018 – winner of the Best Poster Presentation Award);
- One paper titled “Self-cleaning thin films with controlled optical properties based on WO3-rGO” was submitted to the ISI Journal Ceramics International.